Misc
Visualized: The 4 Billion Year Path of Human Evolution
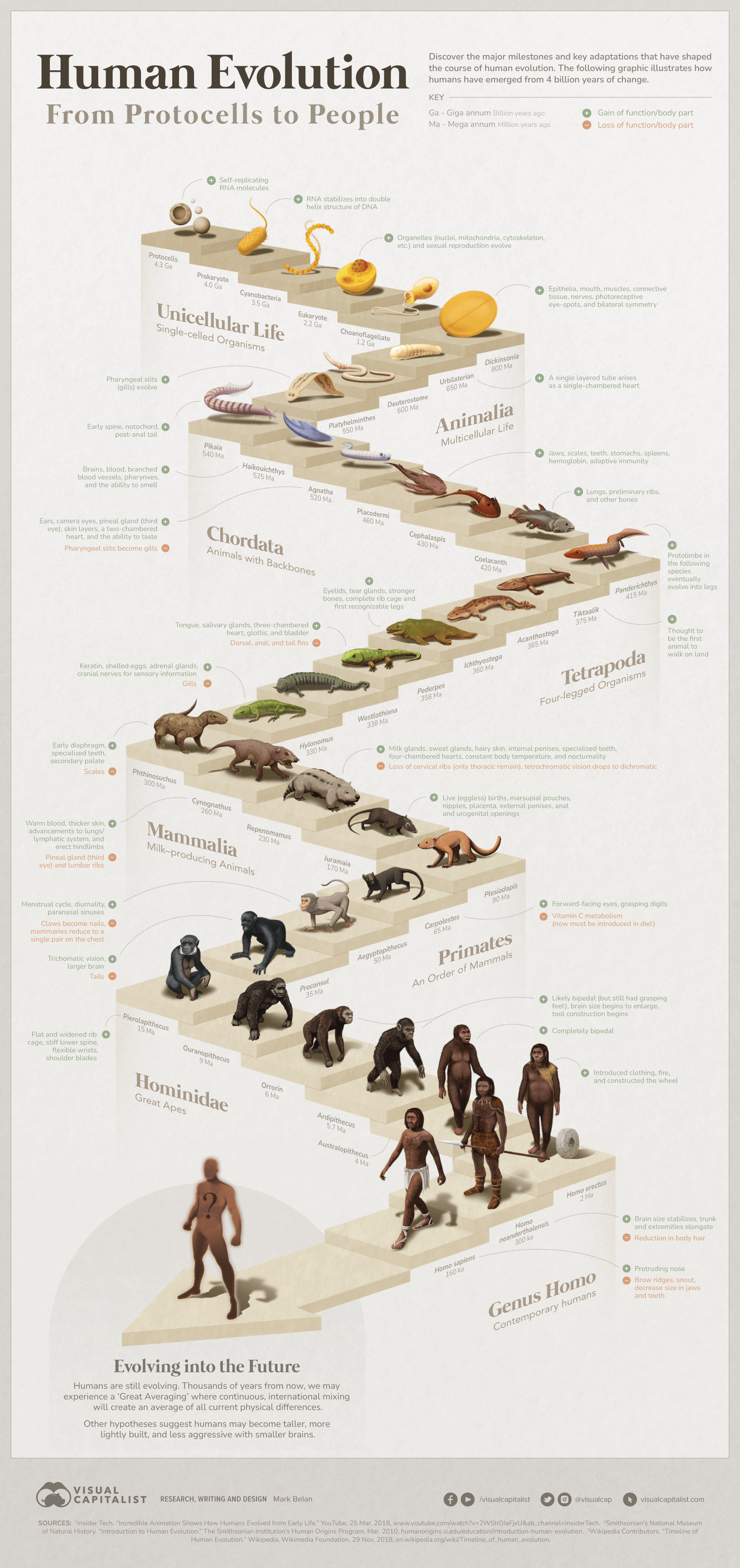
The 4 Billion Year Path of Human Evolution
The story of human evolution is a fascinating one, stretching back in an unbroken chain over millions of years.
From the tiniest protocells to modern humans, our species has undergone a remarkable journey of adaptation, innovation, and survival.
In this article, we take a look at the key developmental stages in the evolution of life on Earth that led to the emergence of Homo sapiens—us!
From Protocells to People
Evolution is the result of millions of minute mutations over millions of years, but the evolutionary process that created us can bucketed into a few key categories.

1. Protocells and Early Microorganisms
The first life forms on Earth were simple, single-celled microorganisms known as protocells. These precursor cells lacked a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles, and they had simple genetic proteins called RNA.
Over time, RNA complexified into the more stable DNA. Protocells slowly developed specialized organelles, becoming more complex microbes that would eventually form eukaryotes – the complex, unicellular organisms that would birth a diverse array of life forms, from simple sponges to complex animals.
2. The First Animals
Dickinsonia is the earliest example of an animal we know of. Though it was a simple, flat creature that lacked a mouth or digestive system, it symbolizes the first multicellular organism of substantial complexity.
Over time, the first sophisticated organ systems began to arise. Bilateral symmetry emerged, as well as early versions of the nervous and circulatory systems. Simple eyes, called eyespots, also appeared around the time that spinal cords and vertebrate creatures began to emerge.
3. Fish and Tetrapods
One of the most significant developments in the evolution of life was the transition from marine to terrestrial environments.
Up until 500 million years ago, all life was sequestered in the sea. Fish were the first vertebrates and introduced additional organs like stomachs, spleens, and body components like scales, teeth, blood, and more. Bony fish arose, and over time their development brought about sophisticated changes to the skeletal system, eventually producing “proto-limbs” that would enable organisms to walk on land.
Researchers are still unsure which specific organism might have first crawled on land, but candidates share these pre-limb characteristics. Tiktaalik is one popular candidate because it had specialized bones that suggest it could support its own weight while moving out of shallow waters.
These creatures eventually became the tetrapods (“four-footed”), and they had features like four-legs, a backbone, and lungs which could absorb oxygen from air. All the amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals that followed are descendants of the original tetrapods.
4. The First Mammals
Around 200 million years ago, the first mammals emerged. These early mammals were small, shrew-like creatures that lived alongside the dinosaurs. Over time, however, mammals evolved hair, specialized teeth, sweat glands to regulate body temperature, and a more efficient circulatory system.
Mammals also brought about features like nocturnality, mammary glands, external genitalia, and a variety of other features that distinguished them from other living species at the time, like birds or reptiles.
5. The Great Apes and First Homo Species
Around 7 million years ago, the first great apes emerged in Africa. These apes, such as orangutans, gorillas, and chimpanzees, were highly intelligent and social creatures that lived in complex communities. Over time, one lineage of apes would give rise to the first members of the genus Homo, which includes our own species.
The main developmental changes during this time were the full-time bipedalism of apes, increasing brain size, and advanced bone development that enabled dexterity for tool construction and hunting. Inventions like fire and clothing arose early in the Homo genus, and eventually complex language, hair loss, and dramatic facial changes would evolve.
Researchers struggle with resolving the exact progression of the Homo species. Many Homo species existed at the same time, and since many fossil records overlap, resolving which ones came first is an area of intense focus.
The Future of Human Evolution
As humans continue to evolve, we can expect to see significant changes in our physical and cognitive abilities over the next 10,000 years.
With the rise of technology and the increasing interconnectedness of the world, we may see a shift towards a more globalized and homogeneous human population, with less genetic diversity.
This has been described as “The Great Averaging”, where genetic diversity minimizes and we start to become more alike.
Other theories suggest that we might develop features like a taller, lighter build, with smaller brains and a less aggressive personality.
However, as with all evolution, these changes will be shaped by a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and cultural factors. It is impossible to predict exactly how humans will evolve over the next 10,000 years, but one thing is certain: the future of human evolution will be shaped by the choices we make today.
Note: This is a complex topic with new research being published all the time. We’ll continue to dynamically update this graphic to reflect the most recent understanding of evolution.
Misc
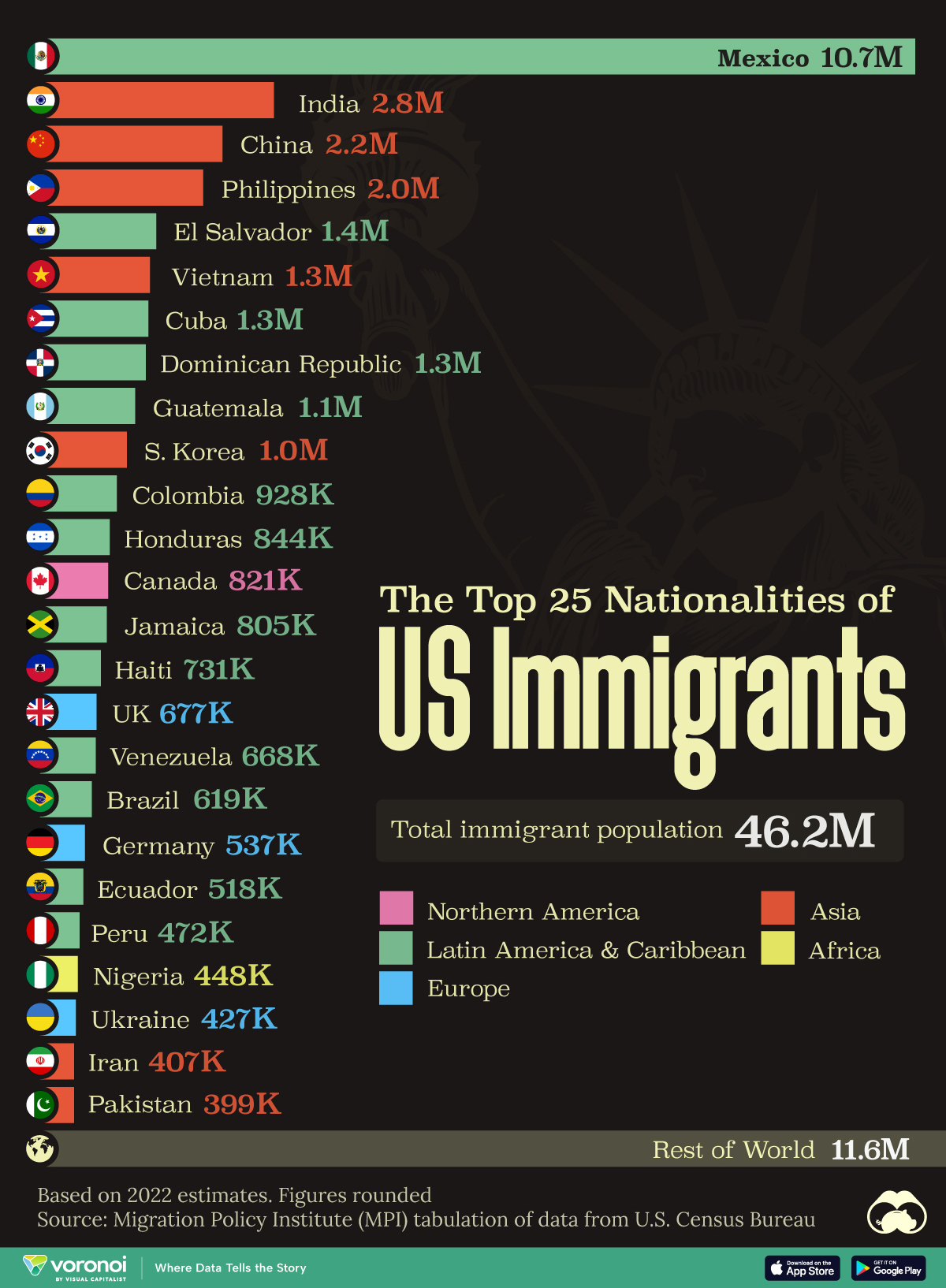
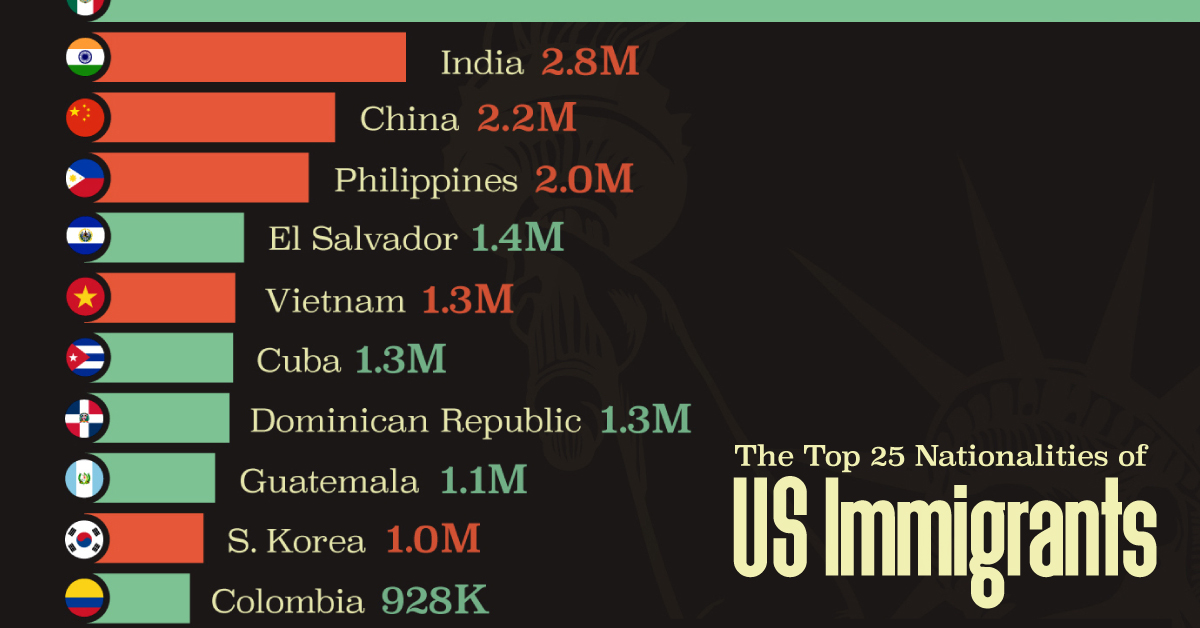
The Top 25 Nationalities of U.S. Immigrants
Mexico is the largest source of immigrants to the U.S., with almost 11 million immigrants.
The Top 25 Nationalities of U.S. Immigrants
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
The United States is home to more than 46 million immigrants, constituting approximately 14% of its total population.
This graphic displays the top 25 countries of origin for U.S. immigrants, based on 2022 estimates. The data is sourced from the Migration Policy Institute (MPI), which analyzed information from the U.S. Census Bureau’s 2022 American Community Survey.
In this context, “immigrants” refer to individuals residing in the United States who were not U.S. citizens at birth.
Mexico Emerges as a Leading Source of Immigration
Mexico stands out as the largest contributor to U.S. immigration due to its geographical proximity and historical ties.
Various economic factors, including wage disparities and employment opportunities, motivate many Mexicans to seek better prospects north of the border.
| Country | Region | # of Immigrants |
|---|---|---|
| 🇲🇽 Mexico | Latin America & Caribbean | 10,678,502 |
| 🇮🇳 India | Asia | 2,839,618 |
| 🇨🇳 China | Asia | 2,217,894 |
| 🇵🇭 Philippines | Asia | 1,982,333 |
| 🇸🇻 El Salvador | Latin America & Caribbean | 1,407,622 |
| 🇻🇳 Vietnam | Asia | 1,331,192 |
| 🇨🇺 Cuba | Latin America & Caribbean | 1,312,510 |
| 🇩🇴 Dominican Republic | Latin America & Caribbean | 1,279,900 |
| 🇬🇹 Guatemala | Latin America & Caribbean | 1,148,543 |
| 🇰🇷 Korea | Asia | 1,045,100 |
| 🇨🇴 Colombia | Latin America & Caribbean | 928,053 |
| 🇭🇳 Honduras | Latin America & Caribbean | 843,774 |
| 🇨🇦 Canada | Northern America | 821,322 |
| 🇯🇲 Jamaica | Latin America & Caribbean | 804,775 |
| 🇭🇹 Haiti | Latin America & Caribbean | 730,780 |
| 🇬🇧 United Kingdom | Europe | 676,652 |
| 🇻🇪 Venezuela | Latin America & Caribbean | 667,664 |
| 🇧🇷 Brazil | Latin America & Caribbean | 618,525 |
| 🇩🇪 Germany | Europe | 537,484 |
| 🇪🇨 Ecuador | Latin America & Caribbean | 518,287 |
| 🇵🇪 Peru | Latin America & Caribbean | 471,988 |
| 🇳🇬 Nigeria | Africa | 448,405 |
| 🇺🇦 Ukraine | Europe | 427,163 |
| 🇮🇷 Iran | Middle East | 407,283 |
| 🇵🇰 Pakistan | Asia | 399,086 |
| Rest of World | 11,637,634 | |
| Total | 46,182,089 |
Mexicans are followed in this ranking by Indians, Chinese, and Filipinos, though most immigrants on this list come from countries in the Latin American and Caribbean region.
On the other hand, only three European countries are among the top sources of U.S. immigrants: the UK, Germany, and Ukraine.
Immigration continues to be a significant factor contributing to the overall growth of the U.S. population. Overall population growth has decelerated over the past decade primarily due to declining birth rates.
Between 2021 and 2022, the increase in the immigrant population accounted for 65% of the total population growth in the U.S., representing 912,000 individuals out of nearly 1.4 million.
If you enjoyed this post, be sure to check out Visualized: Why Do People Immigrate to the U.S.? This visualization shows the different reasons cited by new arrivals to America in 2021.
-

 Mining1 week ago
Mining1 week agoWhere the World’s Aluminum is Smelted, by Country
-

 Culture6 days ago
Culture6 days agoHow Popular Snack Brand Logos Have Changed
-

 Mining7 days ago
Mining7 days agoVisualizing Copper Production by Country in 2023
-
 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoCharted: How Americans Feel About Federal Government Agencies
-
 Healthcare1 week ago
Healthcare1 week agoWhich Countries Have the Highest Infant Mortality Rates?
-
 Demographics1 week ago
Demographics1 week agoMapped: U.S. Immigrants by Region
-
 Economy1 week ago
Economy1 week agoMapped: Southeast Asia’s GDP Per Capita, by Country
-
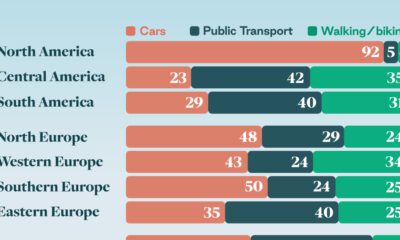
 Automotive1 week ago
Automotive1 week agoHow People Get Around in America, Europe, and Asia