


Evolution is the scientific study of the change in characteristics of a group of organisms over a period of successive generations. In studying the Human Evolution Timeline, scientists have theorized that modern humans evolved from human-like species and other non-human primates that came before us but have now become extinct.
The theory of human evolution is centered around the idea of natural selection, which is accredited to the famous naturalist, Charles Darwin. Natural selection is the process by which an organism’s genetic makeup changes over time to allow it to become better suited to survive in its environment. Darwin was a pioneer in the field of human evolution. One of the key takeaways from Darwin’s theories is that all of the living organisms on Earth share a common ancestor. Moreover, Darwin suggested that the last common relatives of human beings today are apes.
A great deal of genetic evidence was collected surrounding Darwin’s claims about the links between apes and the Human Evolution Timeline. This, in time, has allowed scientists to work out the exact level of similarity between the genetics of apes and humans, which sits around 94%.
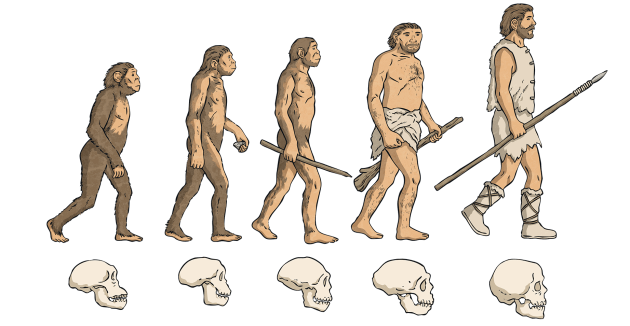
The transition from apes to human beings began with the ability to walk on two legs. This is called bipedalism. One of the earliest known ancestors of human beings, who we will explore more deeply later on in this wiki, was the species, Sahelanthropus tchadensis. It was the Sahelanthropus tchadensis that began to transition into two-legged walking around 6 million years ago. Homo sapiens, which is the species that all human beings currently belong to, did not come about for around 5 million years after this transition took place. During this big gap in the Human Evolution Timeline, lots of different human species lived, evolved, and died. These species gradually changed over time, becoming more developed and more intelligent, and, overall, better suited to live in the world.
From what scientists have gathered, Homo sapiens are believed to have originated on the continent of Africa. Studies suggest that different groups of our human ancestors were scattered across Africa, all living separately from one another until the changing climate forced them to intermingle.
So, now we know what human evolution actually is, we can get into the details of the timeline of human evolution. It all began a long, long time ago, 55 million years ago to be exact…
55 million years ago
The first-ever primitive primates began to evolve.
8 to 6 million years ago
The first-ever gorillas evolved. After this, the different chimp and human lineages begin to separate from one another.
5.8 million years ago
Bipedalism is introduced, as the oldest-known human ancestor is believed to have begun walking on two legs. This ancestor is the species, Orrorin tugenensis.
5.5 million years ago
The primate, Ardipithecus, has common traits with chimpanzees and gorillas. This species lives in forest areas.
4 million years ago
A species of primates known as Australopithecines pop up. These primates have similar-sized brains to chimpanzees but walk bipedally on two hind legs. The Australopithecines are the first human ancestors to have lived in the Savannah.
3.2 million years ago
A group of skeleton fossils discovered in East Africa in 1974 show a specimen of Australopithecus afarensis living in Hadar, Ethiopia. This specimen has since been given the nickname, Lucy.
2.7 million years ago
The primate species, Paranthropus, lived in woods and grasslands at this time. These primates had huge jaws that they would use for eating roots and tough vegetation. Around 1.2 million years ago, this species became extinct.
2.5 million years ago
The species, Homo habilis, appears. This species still shares many features with apes but has a noticeably less protruding face. It was also during this time that hominids began to use stone tools frequently, which they would make by splitting pebbles. Certain hominids also began to develop very meat-heavy diets at this point in the timeline of human evolution. This increase in meat consumption, and the consequent boost in energy that followed, allowed hominids to develop larger brains.
2 million years ago
Evidence of the primate, Homo ergaster, has been found in Africa dating back to this time. This primate had an increased brain volume than earlier species.
1.8 to 1.5million years ago
The species, Homo erectus, is found in Asia. These primates are the first examples we have of hunter-gatherers. They were also the first ones to migrate outside of Africa in large numbers. The brain size of this species is bigger still, at a volume of around 1000 cm3.
1.6 million years ago
This stage in history is believed to have marked the first use of fire, based on evidence found in Kenya. Also, at this time, more complex stone tools were being created and used. These tools remained the most popular form of technology for early humans until around 100,000 years ago.
600,000 years ago
At this time, the species, Homo Heidelbergensis, lives in Africa and Europe. This species of primates had a pretty similar brain capacity to what we have today.
500,000 years ago
The earliest evidence of purpose-built shelters can be traced back to this time. The shelters were wooden huts that were found near Chichibu in Japan.
400,000 years ago
Early humans started using spears in their hunting.
325,000 years ago
The earliest evidence of human footprints can be traced back to 325,000 years ago. These footprints are believed to have been left by three people clambering down the slopes of a volcano in Italy.
280,000 years ago
Stone blades and grinding stones of a more advanced design were invented.
230,000 years ago
It is at this point that Neanderthals begin to appear. They are found across Europe, all the way from Britain to Iran. They eventually became extinct when modern humans took over around 28,000 years ago.
195,000 years ago
This is the first time that modern human beings as we know them, i.e., Homo sapiens, appear. Homo sapiens migrate across Asia and Europe. The earliest evidence of the remains of Homo sapiens dates back to this period. The remains were two human skulls that were found in Ethiopia. At this time, the average brain capacity for Homo sapiens was 1350 cm3.
170,000 years ago
The direct ancestor of all modern human beings alive today is believed to have been living in Africa at this time. Scientists have called this ancestor Mitochondrial Eve.
150,000 years ago
Human beings develop the ability to speak. Evidence has shown that Homo sapiens developed a complex system of speech and symbolism at this time.
140,000 years ago
The first evidence of long-distance trade being carried out can be traced to 140,000 years ago.
50,000 years ago
It is at this point in the timeline of human evolution that human culture starts to develop at a much faster rate. Some cultural changes that took place involved the introduction of ritually burying the dead, making clothes from animal skin, and coming up with more strategic, effective hunting techniques.
33,000 years ago
The earliest evidence of cave art can be traced to 33,000 years ago. The species, Homo erectus also becomes completely extinct in Asia at this time and is replaced by modern humans.
18,000 years ago
A species of small, archaic humans, known as Homo floresiensis, live on the Indonesian island of Flores. These early humans are just over a meter tall and have similarly sized brains to chimpanzees. These humans, unlike chimpanzees, however, did have advanced stone tools.
12,000 years ago
Modern humans make it to the Americas.
10,000 years ago
Agriculture began to develop and quickly became a widespread practice. The rise in agriculture also links to the establishment of the first villages. It is also possible that dogs were first domesticated and kept as pets during this period.
5,500 years ago
The Stone Age comes to an end and the Bronze Age begins. With the beginning of a new age, humans began to work in copper and tin instead of the stone tools that they had used in previous years.
5,000 years ago
This period brings the earliest known example of writing.
4,000 to 3,500 years ago
The Ancient Sumerians of Mesopotamia developed the world’s first-ever civilization.
There are 7 key stages in the history of human evolution. They are as follows:
Human evolution is a fascinating story but children may struggle with some of the vocabulary and complex concepts. Having the right resources can make all the difference in keeping your students engaged and helping them grasp all the concepts. Luckily, we have various informative resources that are suitable for different age groups and easy for you as an educator to implement. Check out the following resources perfect for a unit on the timeline of human evolution:
Take your students on a captivating journey through time, unveiling the mysteries of the Stone Age with a resource designed to pique their curiosity. Our Introduction to the Stone Age PowerPoint does just that! This PowerPoint is a treasure trove of information, delivering a comprehensive overview of the Stone Age. It covers prehistoric time periods, Stone Age geography, housing, clothing, diet, and lifestyle, offering a well-rounded understanding of the era. The inclusion of interesting facts and vivid illustrations adds a layer of excitement to make the learning experience both informative and enjoyable.
Moving beyond traditional teaching methods, we have the Early Humans Circle Foldable for 3rd-5th Grade – a resource that transforms learning into an interactive and creative experience. This activity encourages hands-on exploration as students are required to research the different stages of early humans and use the foldable to record their findings. The interactive nature of this resource taps into various learning styles, ensuring that students are not passive recipients of information but active participants in their learning journey.
Check out this fascinating teaching wiki, where you can learn about Time Periods in History! A great page for the perfect overview of different time periods.
Enjoyed these resources about the Human Evolution Timeline? To access more of our resources sign up for a Twinkl account today. You’ll not only gain access to our treasure trove of educational materials but also become part of a community committed to making learning an exciting and enriching experience!