Complete Plant Morphology with Body Structure and Anatomy
Plants are plants that are cultivated. Plants are living creatures that can produce their own food. All types of plants, ranging from small to very large trees have anatomical or structural similarities. Plant anatomy consists of roots, stems, leaves, flowers and fruit.
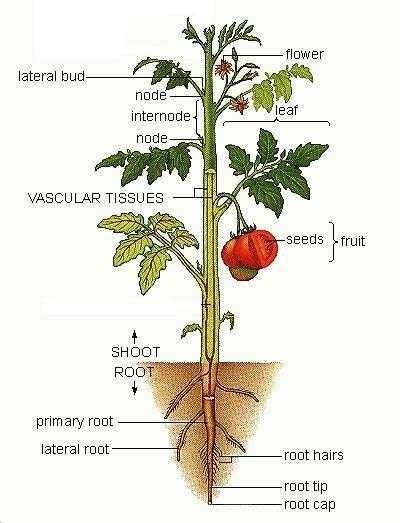
Morphology of Plant Body Structure
The structure of the plant body consists of roots, stems, leaves, flowers and fruit. The root of the plant consists of a root hood, root tip, root hair. Plant roots consist of two types: primary root and lateral root. The primary root is the main root while the lateral root is the root that grows from the primary root.
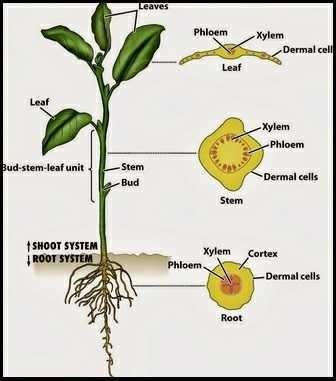
The stem of the plant is the tanman part that grows on the root or grows on the surface of the planting medium (soil, water or other planting media). In the stem of the plant there is a network of bottom trunk (ground tissue) that connects the root with the stem of the upper plant and the upper plant organs. Other tissues contained in the stem are vascular tissue consisting of xylem (water transport network) and phloem (transport network of photosynthesis). The whole body of the plant is protected by epidermal cells.
In the stem of the plant there are leaves, then at the time of adult plants, on the stem organs will grow and develop flowers. Flower plants have pistils and stamens, and in the right conditions, the pistil will be pollinated by pollen so that it becomes fruit. In good quality fruits will grow seeds as the forerunner of the next generation of plants.
Plant Morphology Cell Structure
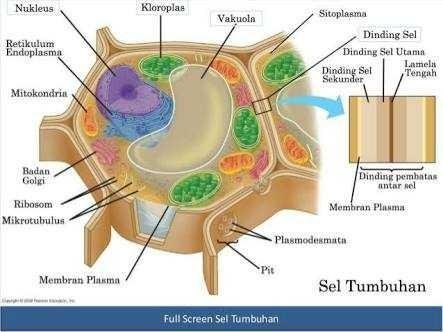
Cells are the smallest organizational unit on which life is based. All life functions are organized and take place within the cell. Cells can function autonomously (independently or independently) provided all life needs are met. Living things (organisms) can be composed of a single cell (unicellular, eg bacteria, and some fungi and protozoa) or composed of many cells (multicellular). In multicellular organisms there is a division of the tasks of its constituent cells, and is the basis for the classification of living things.
In 1665, a British scientist Robert Hooke studied thinly sliced corks using his own designed microscope. The word cell is derived from the Latin word cellulae which means 'small rooms.'
Then a microbiologist, Anton van Leeuwenhoek, observed microbial objects and microorganisms and observed that there is "another life in the world" that is microbial life (small organisms) that no human has ever seen before. This discovery is the basis for the development of the current important biological field of microbiology (the study of the development and growth of living things small / microbial).
The development of the microscope for the next nearly 200 years has provided an opportunity for experts to examine the organisms of living things. Various studies have been conducted by 2 German scientists Matthias Schleiden (plant experts, 1804-1881) and Theodor Schwann (animal expert, 1810-1882). They concluded that every living being is made up of cells. Later in 1885 a German scientist, Rudolf Virchow, observed that cells can divide and form new cells.
Cell structure
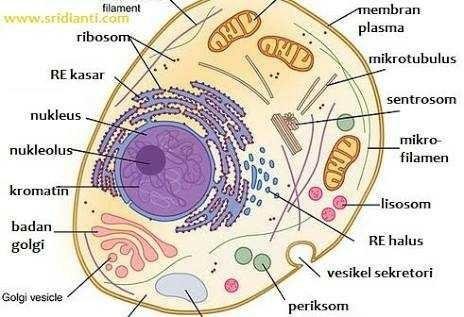
The structure of living cells generally consists of at least the organelles of the cell membrane, the cytoplasm, and the nucleus of a cell or nucleus. Cytoplasm and nucleus together and continuously form protoplasm. In the cytoplasm there are various organelles. Plant cells, algae and prokaryotes develop cell walls while animal cells do not have cell walls. Some prokaryotic organisms have flagella in their cells to facilitate movement.
Similarly with cells. Cells have organs called organelles (meaning 'small organs'). Here are the various objects in the cell (especially cytoplasm) that are classified as organelles:
Mitochondria.
Plastids (only plant cells and some algae)
Golgi or Golgi or diktiosomal bodies
Ribosome
The endoplasmic reticulum
Peroxisomes
Vakuola
Plant morphology is a science that studies the physical form and structure of the body of plants, morphology derived from the Latin morphus meaning form or form, and logos which means science.Morphology of plants is different from the anatomy of plants that specifically study the internal structure of plants at the microscopic level. 3] Plant morphology is useful for identifying plants visually, so the vast diversity of plants can be identified and classified and named for each group formed, the science of classification and the naming of plants is taxonomy
SOURCE REFERENCE
https://id.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Morfologi_tumbuhan
https://www.google.co.id/amp/s/rifqisalafuddin.wordpress.com/2012/03/01/morfologi-tumbuhan-akar-batang-daun/amp/
http://www.academia.edu/11445896/morfologi_tumbuhan
Here's my post about morphology. Maybe post will be sustainable about the benefits of morphology .. If a friend likes posting follow me and follow
my @sahlan89