Table of Contents
The basic and basic part of life is a cell. If at the cellular level, we differentiate between living organisms, then the smallest independent component that may appear would be a cell. Cells can be defined as the basic unit of life that is responsible for all life processes.
The cell has a reproductive quality and is thus known as the basis for life. Inside each cell, there is a fluid known as the cytoplasm, which is trapped by membranes. In the cytoplasm, several biomolecules are present, such as lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins.
Existing cellular structures are called cell organelles that are embedded in the cytoplasm. Cells can come in a variety of shapes and sizes, basically like building blocks.
Organelle, also called the small organ, is a small biological structure that performs a special function within the cell. Cell cells and components include important cell components such as ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, nucleus, chloroplast, etc. Cell Organelles and Components play a vital role in cell function and function.
Cell Organelles Description
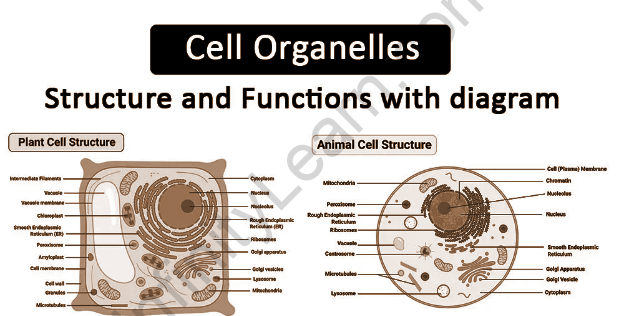
The parts of a cell are called cell organelles. These cells are organelles that have both a membrane (a layer) and non-membrane (non-film-bound) organelle, which are present within the cells and differ in structure and strength. They connect and do well to make the cell work better. A few of them work by providing status and support, while others help with cell mobility and production. The various organisms inside the cell are divided into three categories, such as the presence or absence of membranes –
- Organelles Outer Membrane: Cell membrane, Ribosomes, and Cytoskeleton are non-binding cell organelles. They are present in both prokaryotic cells and therefore eukaryotic cells.
- Single Membrane-Bound Organelles: These are Vacuole, Lysosome, Golgi bodies, Endoplasmic Reticulum only present during eukaryotic cell.
An organelle is composed of double-film or double-membrane organelles: The nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplast are two layers bound only by organelle during the eukaryotic cell.
Cell organelles/structures can be divided into three types:
General cell organelles: General cell organelles are found in both animal and plant cells – cell membrane, reticulum, Golgi apparatus, cytosol, nucleus, mitochondrion, cytoplasm, lysosome, rough and smooth endoplasmic peroxisome, and cytoskeleton.
- Temporary organelle cells: Temporary organelle cells are found in certain stages of the cell life cycle – chromosome, autophagosome, centrosome, and endosome.
- Cells of organelles cells: Cells of a specific type of cell are found only in plant cells – the central vacuole, chloroplast, and cell wall.
List of Cell organelles
- Cell membrane
- The Cell Wall
- The nucleus
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Golgi Apparatus
- Centriole
- Lysozyme
- Microfilaments
- Chloroplast
- Cytoplasm
- Cytoskeleton
- Middle threads
- Plasmodesmata
- Endosomes
- Microtubules
- Final granules
- Plastids
- Mitochondria
- Vacuole
- Peroxisomes
- Ribosomes
- Cilia and Flagella
- Vesicles
- Microvilli
List of Cell Organelles and their functions
- Plasma Membrane
The cell wall is also called the cell wall or cytoplasmic membrane made up of lipid bilayer and proteins.
The plasma membrane is composed of both plant and animal cells, acting as a selective membrane that can penetrate. This means that it only allows the installation of selected items inside and outside the cell according to the requirement. In the animal cell, the cell wall works by providing shape and protection of the cell’s internal contents.
- Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is present in both plant and animal cells. They are liquids and jelly-like substances that fill the void between the cell wall and the nucleus. They are a mixture of water, organic and inorganic compounds. The cytoplasm is one of the most important cells in the cell. you can find all the organelles cell embedded in the cytoplasm. These cell organles contain enzymes, which are primarily responsible for regulating all metabolic activities that take place within a cell and are the site of many chemical reactions within a cell.
- The nucleus
The nucleus can be defined as a double-membraned organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Structurally the nucleus is round, covered with a nuclear membrane and colored black. It resembles the shape of a cell membrane and forms a wall between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Nucleoli are small circular bodies. But that is not all, as you can find chromosomes in the nucleus.
Chromosomes are thin and fibrous structures that carry another important structure called a gene. Genetics is a genetic unit in living organisms that is, it helps to inherit traits from one generation (parents) to another (offspring). The primary function of the nucleus is to monitor cellular activity that mediates metabolism and growth through genetic DNA information. Nucleoli within the nucleus are responsible for the fusion of proteins and RNA.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum may be a fluid-filled membrane of membranes. They are involved in the transport of material throughout the cell and are known as the cell transport system.
There are two different types of Endoplasmic Reticulum:
- Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum – Composed of cisternae, tubes, and vesicles, located throughout the cell and involved in protein synthesis.
- Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum – They are the last organelle, related to the synthesis of lipids, steroids, and are responsible for removing toxins from the cell.
- Mitochondria
Mitochondria two-pore organelles can be found in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells that provide energy by breaking down carbohydrates and sugar molecules, hence the name “Energy House of a Cell.”
- Plastids
Double-membered organelle Plastids are found within plant cells and algae. These plastids play an important role in food production and storage. Plastids usually contain pigs that are commonly used in the process of photosynthesis. These colours have the function of changing the colour of the cell.
Below is a list of key plastics and their function –
- Leucoplasts
Leucoplasts can be found in non-photosynthetic tissues of plants that act as a storehouse of protein, lipid, and starch.
- Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are an extended organelle wrapped in phospholipid film. Chloroplast forms a type of disk, so stroma is a liquid inside the chloroplast that binds to DNA. All chloroplast has a green colour called chlorophyll that is used in photosynthesis. Chlorophyll absorbs sunlight energy and uses it to convert CO2 and water into sugar.
- Ribosomes
Ribosomes are known as macro-molecular mechanisms found in almost all living cells of biological protein synthesis. Hence, ribosomes are also known as cellular protein industries. Ribosomal RNA and Ribosomal proteins are 2 components that combine to form ribosomes. The primary function of ribosomes involves the binding of proteins to all living cells that ensures cell survival.
- Golgi Apparatus
Golgi Apparatus also called Golgi body organelle is a complete component of eukaryotic cells involved in the distribution of compound macromolecules in various cell components.
- Bacteria
Microbodies are membrane-bound, minute, vesicular organelles, found in plant and animal cells. They contain various enzymes and proteins and can only be seen under a microscope.
- Cytoskeleton
It is an endless network of filamentous proteinaceous structures that run throughout the cytoplasm, from the nucleus to the cell wall. It is found entirely in living cells, especially within eukaryotes. The cytoskeleton network is made up of different types of proteins that can quickly divide or disperse depending on the need for cells. Essential skills include providing the structure and protection of machinery from the cell against the defect, a contractual concept of fibres aids in movement during cytokinesis.
- Cilia and Flagella
Cilia are hair-like specimens, small structures, which exist outside the cell membrane and act as oars or move cells or ECF. Flagella are somewhat larger and more responsible for the movement of cells. The eukaryotic flagellum varies from prokaryotic partners to structure. The centre of the cilium and flagellum is known as the axoneme, which consists of nine sets of slightly rotating microtubules and a series of intermediate running microtubules. The middle tubes are connected to the scaffold and embedded in the middle shirt. One of the peripheral microtubular pairs is connected to the central pouch by a radial speaker. So there is a complete set of 9 radial speakers. The cilia and flagella come out of the centriole-like forms known as the basal bodies.
- Centrosome and Centrioles
The centrosome organelle is composed of two distinct structures known as centrioles. Each centriole contains 9 peripheral fibrils that are evenly separated from the tubulin protein, so fibril can be a set of interconnected triplets. The core, part of the centriole, is understood to be a hub and contains protein. The hub connects the peripheral fibrils with a radial spoke, made up of proteins. Centrioles form the primary cilia and flagella bodies produce spinning fibres during cell division.
- Vacuoles
Vacuoles are often seen as storage bubbles in unexpected forms found in cells. They are liquid organelle-filled films. Vacuole stores food or the distribution of nutrients that a cell may need in order to survive. In addition, it also stores contaminated products. Byproducts are finally released by vacuoles. Thus, the rest of the cell is protected from contamination. Animal and plant cells have different sizes and numbers of vacuoles. Compared with animals, plant cells have a larger vacuole.
Organelles of the Endomembrane System
The Endomembrane System is a compound of three large organisms that together form a system within a cell. These organelles work together to perform various cellular functions such as manufacturing, packaging and exporting certain cellular products. Organelles of the endometrium system include the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and vesicles.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum
The continuous channels of the nucleus covering the nucleus and composed of the same lipid bilayer are called the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). It provides corridors for all cells that work in transporting, assembling, and storing building materials.
- Golgi Apparatus
It is responsible for filtering, processing, and exporting cellular products from the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER), such as the post office. Golgi apparatus resembles flattened discs, almost stacks of unusual pancakes. Golgi machines have two different sides and each has a different role.
- Lysosomes
An organelle that contains enzymes that break down and break down essential cellular components, such as damaged organelle, is called the lysosome. Golgi-derived protein products such as digestive enzymes are intended to stay inside the cell to break down the certa.
FAQ’s
What is the cell organelle called Powerhouse cell?
Mitochondria is a cell organelle and is called the Powerhouse of the cell as it breathes cells and produces energy molecules called ATP or Adenosine Triphosphate.
Where do we get Chloroplasts and Chromoplast pigments from plants?
Chloroplasts and Chromoplasts plastids are present in all plant cells. Chloroplasts are green, present in leaves, green stems, etc. Colourful pigment chromoplasts are present in all coloured parts of the plant such as flowers and fruits, etc.
Why are Lysosomes known as suicide bags?
Lysosomes are called suicide bags because they are able to break down or digest all the waste, dead and damaged cells.





